Corneal stem cell therapy is emerging as a groundbreaking solution for individuals suffering from severe corneal injuries. This innovative treatment utilizes cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) to restore damaged corneal surfaces, offering new hope to those with eye damage once deemed untreatable. By leveraging stem cell therapy, researchers at Mass Eye and Ear have successfully demonstrated a high success rate in restoring corneal integrity, showcasing its potential for revolutionizing eye damage treatment. With treatment protocols that carefully harvest limbal stem cells from healthy eyes, this method ensures a personalized approach to corneal injury recovery. As ongoing clinical trials continue to shed light on its effectiveness, the promise of CALEC surgery is reshaping the landscape of vision rehabilitation for patients affected by corneal damage.
Limbal stem cell therapy, a term often synonymous with corneal stem cell therapy, represents a pioneering step forward in ocular repair methods. This technique focuses on regenerating the limbal epithelial cells essential for maintaining a healthy cornea, particularly following injuries or diseases that compromise vision. Utilizing advanced methods such as cultivated stem cells from a patient’s unaffected eye, these therapies aim to restore the eye’s natural function and alleviate persistent vision problems. By providing a regenerative approach to corneal rehabilitation, researchers are addressing the critical need for effective treatments in eye health. The success of CALEC surgery exemplifies the potential of stem cell-based interventions in healing corneal injuries and enhancing the quality of life for affected patients.
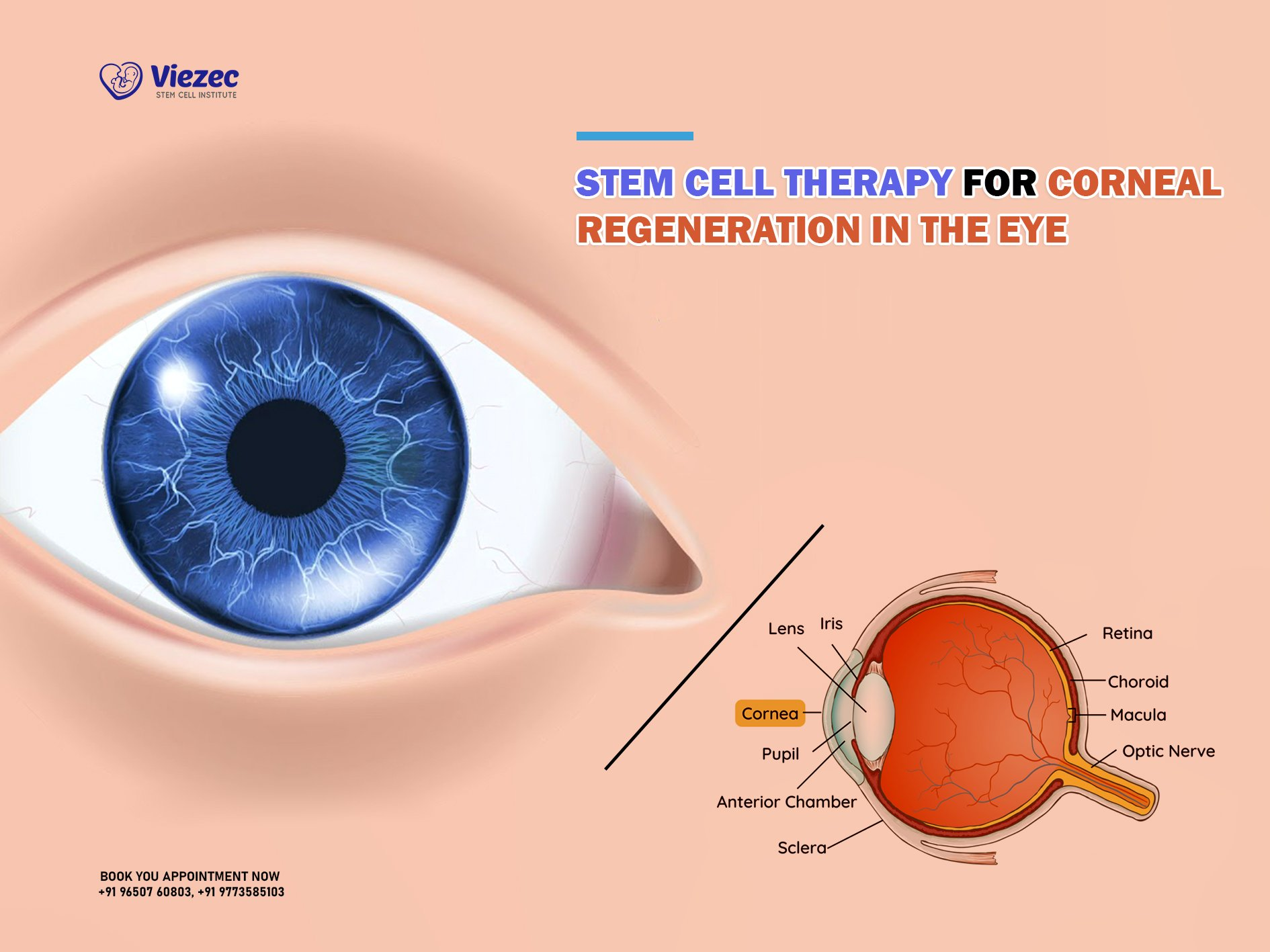
Understanding Corneal Stem Cell Therapy
Corneal stem cell therapy is a groundbreaking development in ophthalmology, especially for patients with corneal injuries that have led to significant vision loss. This innovative treatment utilizes cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC), which are derived from a healthy eye, to regenerate the corneal surface. By enhancing the healing process through stem cell technology, patients previously deemed untreatable are given a new lease on life. The use of limbal stem cells is crucial, as they are essential for maintaining the cornea’s integrity and clarity, and their depletion can lead to a series of complications, including persistent pain and vision impairment.
The success of corneal stem cell therapy, particularly CALEC, has demonstrated high efficacy in restoring the corneal surface in clinical trials. Following rigorous testing and studies, researchers have found remarkable success rates. For example, within a follow-up period of 18 months, patients exhibited a success rate in excess of 90%, showcasing the potential of stem cell therapy as a viable option for those suffering from severe corneal damage. These promising results have sparked further interest in expanding research to include larger populations and exploring the genetic makeup of the limbal stem cells used in these procedures.
The Clinical Trial Process for CALEC Surgery
The clinical trial for CALEC surgery represents a significant milestone in eye damage treatment, involving a meticulously designed process to ensure patient safety and the effectiveness of the therapy. Initially authorized by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the trial marked the first human implementation of such a treatment for corneal injuries in the U.S. The trial flounders not just in establishing the treatment’s safety but also in setting the groundwork for future studies aimed at achieving broader accessibility to stem cell therapies for eye conditions.
Throughout the trial, meticulous care was taken to track the progress and outcomes of participants who underwent CALEC surgery. Remarkably, researchers found that half of the patients experienced complete restoration of the cornea within the first three months. This clinical trial not only showcased the critical role of advanced research in the field of ophthalmology, but it also highlighted the need for ongoing studies to explore other approaches, such as utilizing allogeneic grafts from donor eyes for patients with damage to both eyes. Ensuring the future viability of CALEC surgery largely depends on empirical evidence gathered through future clinical studies.
Implications of CALEC for Eye Injury Recovery
The ramifications of successful CALEC therapy cannot be overlooked when considering the broader scope of corneal injury recovery. Stem cell-based treatments represent a paradigm shift in the management of eye damage, providing hope to countless individuals who have faced the debilitating effects of corneal diseases. By addressing the root cause of vision impairment through the regeneration of limbal stem cells, CALEC offers a potential alternative to conventional approaches, such as corneal transplants, which are limited by availability and risk of rejection.
Beyond immediate recovery, the implications of CALEC extend to enhancing patients’ quality of life, improving visual acuity, and alleviating chronic pain associated with corneal damage. As more clinical research validates the efficacy of this therapy, it sets the stage for developing comprehensive treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs. Enhanced awareness and understanding of corneal stem cell therapy could propel innovation in eye care, ultimately leading to increased funding and research opportunities aimed at broadening its application.
Advances in Stem Cell Therapy for Corneal Diseases
Recent advancements in stem cell therapy have fundamentally transformed the management of various corneal diseases, including those resulting from injuries and degenerative conditions. By applying cutting-edge techniques and biotechnologies, researchers have made it possible to isolate and expand limbal stem cells effectively, leading to greater treatment efficacy and patient outcomes. Innovations in the manufacturing processes for CALEC grafts illustrate the intricate balance between scientific research and practical application, ensuring that the highest quality cells are available for transplantation.
Furthermore, with ongoing research and clinical collaborations across prestigious institutes, the landscape of eye damage treatment is rapidly evolving. Researchers are exploring potential enhancements to the CALEC methodology, including the possibility of creating a universal donor pool from cadaveric limbal stem cells. This could significantly increase treatment availability for patients worldwide. As exploration and understanding of stem cell therapy flourish, it offers promising pathways for uncovering novel treatment mechanisms, potentially revolutionizing how corneal diseases are treated.
Limbal Stem Cells: A Vital Component of Eye Health
Limbal stem cells play a crucial role in maintaining the health and functionality of the cornea. These cells reside in the limbus, the border area between the cornea and the sclera, and are responsible for regenerating the surface epithelium of the cornea. When an injury or disease depletes these important stem cells, it can lead to limbal stem cell deficiency, resulting in a damaged cornea that often cannot heal. Understanding the function and importance of limbal stem cells has led to the development of innovative therapies like CALEC, which seeks to replenish these critical cells and restore normal corneal function.
The emphasis on limbal stem cell health has prompted further investigation into the pathways that hinder their function and proliferation. As ongoing research unpacks the biological mechanisms behind stem cell functionality in the eye, researchers are better equipped to design targeted therapies. Ensuring a robust supply of healthy limbal stem cells not only boosts the possibilities for corneal repair procedures but also establishes a foundation for advancing regenerative medicine approaches in ophthalmology.
Challenges and Future of Corneal Stem Cell Treatments
Even with the groundbreaking progress made in corneal stem cell therapy, several challenges remain. One of the main obstacles is the limited availability of healthy limbal stem cells, as the current methods require a biopsy from the unaffected eye. This restriction confines the potential patient population eligible for treatment. Future research must address how to create a sustainable supply of limbal stem cells that can be utilized across a broader demographic without relying solely on the patient’s own cells.
Additionally, as CALEC surgery enters its next phases of research and potential commercialization, considerations regarding regulatory approval and ethical sourcing of stem cells must be taken into account. Advocating for enhanced trial design and larger sample sizes will provide more robust data to support the efficacy and safety of these innovative treatments. Furthermore, stakeholder collaboration, including clinicians, researchers, and regulatory agencies, is essential in navigating potential hurdles and establishing corneal stem cell therapy as a standard treatment option for vision restoration.
The Role of FDA Approval in CALEC Surgery
The journey of CALEC surgery from laboratory innovation to clinical application is largely dependent on securing FDA approval, which ensures that treatments are safe and effective for public use. An integral aspect of the clinical trial process involves obtaining this regulatory endorsement, essential for legitimizing the treatment within the medical community. As CALEC shows promising results in restoring corneal surfaces, the pressure mounts for thorough assessment to determine its rightful place within ocular therapeutics.
Achieving FDA approval involves a multi-tiered evaluation of clinical trial data, including long-term efficacy and safety reports. The positive outcomes from the Mass Eye and Ear study emphasize the need for continued focus on rigorous testing protocols and ethically sound practices in clinical trials. This process is crucial not only for the benefit of patients suffering from corneal injuries but also for establishing trust within the medical community regarding stem cell therapy as a viable treatment modality.
Collaboration in Eye Care Research
Collaboration across various research institutions plays a pivotal role in enhancing the development of effective eye treatments. The collaborative efforts between Mass Eye and Ear, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and other leading organizations have been beneficial in refining the techniques used in CALEC surgery. Such teamwork fosters an environment of shared knowledge and resources, allowing researchers to overcome obstacles encountered in the journey toward improving corneal health and advancing stem cell technology.
Global partnerships are also vital for propelling advancements in eye care. Engaging collective expertise in various fields—including molecular biology, ophthalmology, and regenerative medicine—expands the potential for innovative solutions. As researchers unite to tackle the complexities of corneal diseases and injuries, the future of therapies grounded in stem cell science looks increasingly promising, paving the way for new treatments that could enhance the lives of countless patients worldwide.
The Impact of Visual Acuity in Corneal Treatments
Visual acuity is a critical component of assessing the success of any corneal treatment, including the CALEC surgery. The improvement in patients’ vision post-procedure is not only a marker of the treatment’s effectiveness but also an essential factor in restoring quality of life. The data from clinical trials indicated varying levels of improved visual function among participants, showcasing the therapy’s diverse impact. Such outcomes reinforce the practical significance of stem cell therapy in managing corneal damage, as patients often experience not just restored sight, but also a renewed sense of independence.
Measurable improvements in visual acuity also provide insight into the mechanisms underlying corneal health and recovery. By understanding how CALEC surgery influences sight restoration, researchers can enhance current treatment methodologies and develop future interventions. As ongoing studies continue to analyze the nuances of visual outcomes, the foundational knowledge of how to boost patient outcomes effectively will be critical for shaping subsequent clinical practices in ocular stem cell treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is corneal stem cell therapy and how does CALEC surgery work?
Corneal stem cell therapy, specifically the Cultivated Autologous Limbal Epithelial Cells (CALEC) procedure, involves harvesting limbal stem cells from a healthy eye, expanding them into a graft, and transplanting this graft to repair a damaged cornea. This innovative therapy has shown over 90% effectiveness in restoring the cornea’s surface in clinical trials.
Who can benefit from corneal stem cell therapy treatments like CALEC?
Individuals suffering from corneal injuries due to trauma, chemical burns, or infections, especially those with one affected eye, can benefit from corneal stem cell therapy. CALEC surgery is specifically designed for patients with limbal stem cell deficiency, which leads to corneal surface damage.
Are there any risks associated with corneal stem cell therapy and CALEC surgery?
While CALEC surgery has demonstrated a high safety profile in clinical trials, potential risks include the possibility of minor adverse events such as infections. Serious complications were not reported in this trial, emphasizing the procedure’s safety.
How long does it take to see results from corneal stem cell therapy?
Results can be seen as early as three months post CALEC surgery, with more significant improvement at the 12- and 18-month follow-ups. Success rates for complete corneal restoration were noted at 50% at three months, rising to 77-79% at 12 and 18 months respectively.
Is corneal stem cell therapy with CALEC surgery available in the U.S. now?
Currently, CALEC surgery remains experimental and is not yet available at Mass Eye and Ear or other U.S. hospitals. Further studies are ongoing before it can be submitted for federal approval.
What improvements in vision have patients experienced after corneal stem cell therapy?
Patients who underwent CALEC surgery reported varying degrees of improvement in visual acuity. Although complete restoration of corneal surfaces was significant, the resulting vision enhancements are individual and can differ among patients.
What is the procedure for harvesting limbal stem cells in CALEC surgery?
In CALEC surgery, limbal stem cells are harvested through a biopsy from the unaffected eye. This process involves careful removal of a small amount of healthy tissue, which is then expanded in a controlled environment to create a cellular graft for transplantation into the damaged eye.
What future developments are expected for corneal stem cell therapy?
Future research may include the establishment of an allogeneic process where limbal stem cells from cadaveric donors are used, potentially allowing treatment for patients with damage to both eyes. Additional clinical trials are essential for expanding access to this innovative therapy.
How effective is corneal stem cell therapy for treating blinding corneal injuries?
Research indicates that corneal stem cell therapy using CALEC has over a 90% effectiveness rate in restoring the cornea’s surface, providing new hope for patients with previously untreatable blinding corneal injuries.
Who are the primary researchers behind CALEC surgery?
The primary investigators behind the development of CALEC surgery include Ula Jurkunas and Reza Dana, who are associated with Mass Eye and Ear and are leading efforts in innovative treatments for corneal injuries using stem cell therapy.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Study Focus | Clinical trial of CALEC surgery for treating corneal injuries using stem cells. |
| Principal Investigator | Ula Jurkunas, Mass Eye and Ear. |
| Treatment Overview | Transplantation of cultivated limbal epithelial cells (CALEC) developed from healthy eye stem cells. |
| Trial Results | 92-93% success rate in restoring corneal surfaces over 18 months with significant improvements in vision. |
| Patient Requirement | Patients must have only one affected eye for biopsy purposes. |
| Future Prospects | Potential for treating patients with bilateral eye damage through allogeneic manufacturing. |
| Safety Profile | No serious adverse events reported; minor complications mostly resolved quickly. |
Summary
Corneal stem cell therapy, known as cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells (CALEC), represents a groundbreaking approach in restoring damaged corneas. This innovative treatment demonstrates a remarkable 92-93% success rate in clinical trials, offering hope to patients with previously untreatable eye injuries. With ongoing research indicating its effectiveness and safety, CALEC could redefine therapeutic options for corneal damage, paving the way for broader applications and potential FDA approval in the future.