Suicide prevention for older adults is an urgent issue that deserves immediate attention as this demographic, particularly those aged 75 and over, experiences the highest rates of suicide across all age groups. Despite their increasing vulnerability, resources tailored to meet the mental health needs of the elderly are alarmingly scarce. Studies reveal that many well-known suicide prevention organizations often overlook geriatric suicide awareness, leaving seniors with few options when they seek assistance. This imbalance in available online resources for the elderly can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and despair, which are prevalent in this age group. To address these critical issues, we must prioritize creating accessible mental health resources for older adults to reduce the rising suicide risk among seniors and foster a supportive environment that encourages open discussions about mental health in the elderly.
In the realm of elder care, awareness surrounding the prevention of self-harm in aging populations is becoming increasingly critical. Many seniors face unique challenges that can lead to heightened feelings of isolation, making it essential to improve access to mental health support tailored specifically for them. The ongoing neglect in addressing the mental wellness of this demographic not only stems from a lack of adequate resources but also from a general unawareness within the community about the suicide risks seniors face. To combat this, a concerted effort to enhance the visibility of mental health services for older adults is necessary, including the development of specialized online platforms that cater to their needs. As we strive to foster a culture that promotes geriatric mental health, we can significantly contribute to reducing the alarming rates of suicide within this vulnerable age group.
Understanding Suicide Risk in Seniors
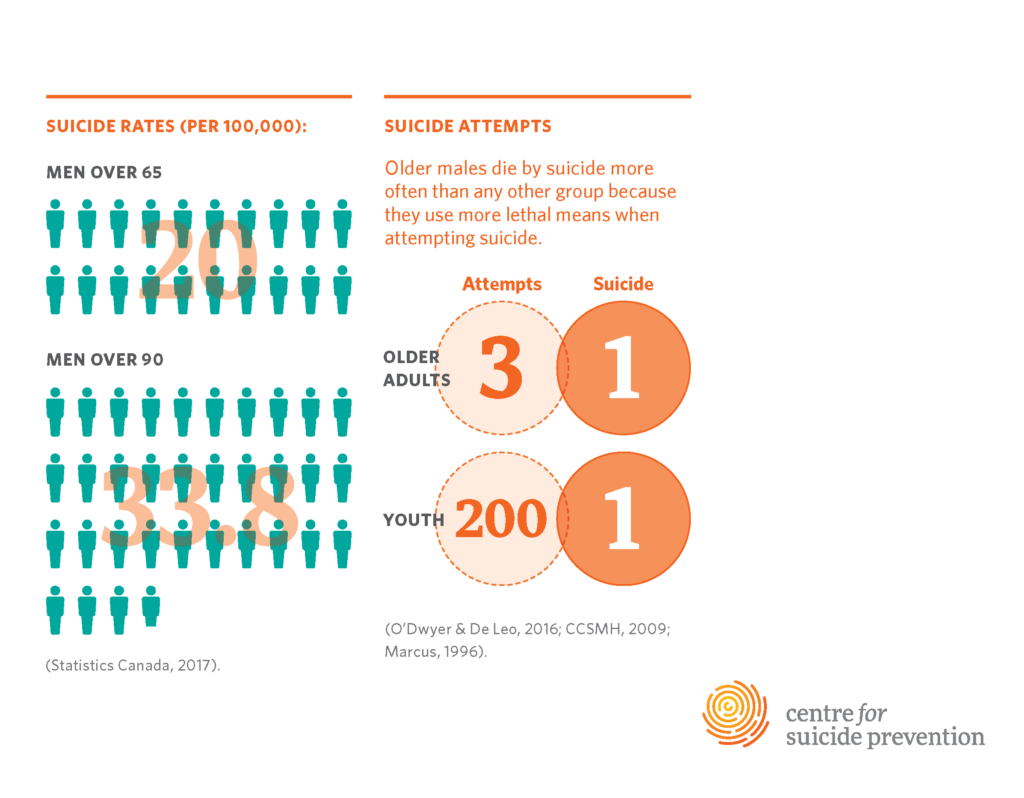
Suicide risk among seniors, particularly those over the age of 75, has reached alarming levels, making it vital for society to recognize the unique challenges faced by this demographic. With a suicide rate of 20.3 per 100,000 as noted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, older adults represent the group with the highest risk. Factors contributing to this heightened vulnerability include social isolation, chronic health conditions, and feelings of hopelessness. Traditional mental health resources often overlook the specific needs of elderly individuals, highlighting an urgent demand for targeted interventions.
Social isolation is a significant factor influencing suicidal thoughts in older adults, as many experience loneliness due to the loss of peers or a lack of family interaction. The stigma surrounding mental health in elderly populations can lead to underreporting and a lack of treatment, resulting in a cycle of suffering that can go unnoticed. Public awareness campaigns focused on geriatric suicide awareness must emphasize the importance of community engagement, fostering connections, and providing accessible resources for seniors to seek help.
The Need for Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
Given the rising suicide rates among older adults, there is a critical need for dedicated suicide prevention efforts targeting this age group. The collaborative research led by Ipsit Vahia from McLean Hospital highlights the significant gap in available resources for seniors seeking help. Many well-known suicide prevention organizations predominantly cater to younger populations, leaving older adults with few options for support. It’s essential that these organizations reevaluate their outreach strategies and develop resources tailored specifically to the geriatric demographic’s needs.
Suicide prevention for older adults must encompass comprehensive approaches that understand the multifaceted nature of their mental health challenges. This includes addressing the systemic biases against elderly individuals and integrating their healthcare needs into prevention programs. Campaigns should utilize online platforms effectively, as many older adults now turn to the internet for health information. By providing easily accessible resources and encouraging dialogue about mental health, society can start to break the barriers that isolate seniors during their most vulnerable moments.
Implementing Online Resources for Elderly Mental Health
As older adults increasingly rely on the internet for health-related queries, the importance of optimizing online resources for elder mental health cannot be overstated. Many existing platforms fall short in meeting the accessibility and usability needs of older individuals, making it difficult for them to find vital information about mental health and suicide prevention. Simplifying website navigation and ensuring the availability of information in larger text can enhance user experience significantly. Additionally, providing dedicated sections focusing specifically on senior mental health will empower older adults to seek the help they need.
Mental health resources for older adults should also include educational materials that resonate with their unique experiences. Incorporating relatable narratives, testimonials, and practical coping strategies can foster a sense of understanding and relatability. Furthermore, partnerships between local organizations and online resources can facilitate community engagement—offering workshops and seminars that promote mental health awareness among seniors. By utilizing these innovative methods, we can create an ecosystem that supports elderly mental health and burgeons suicide prevention efforts.
The Role of Family in Preventing Suicide Among Seniors
Family members play a pivotal role in the mental health of older adults. They can observe early warning signs of emotional distress or changes in behavior, which are often indicators of suicidality. Encouraging open dialogue about mental health within families is essential, as it helps reduce stigma and fosters an environment where older adults feel comfortable expressing their emotions and seeking help. Educating family members about the signs of depression and suicide risk in seniors arms them with the tools needed to offer appropriate support.
Additionally, families can actively participate in suicide prevention by engaging older adults in meaningful activities and social connections. Regular visits and participation in community events help combat feelings of isolation while also reinforcing the networks that are crucial for emotional support. It’s key to create an atmosphere that prioritizes social interactions and warmth, thereby enhancing the overall mental well-being of older adults and significantly reducing the perceived risk of suicide.
Building Community Support to Reduce Elderly Suicide Rates
Community support networks are essential for reducing suicide rates among older adults. Collaborative efforts between community organizations, healthcare providers, and governmental bodies can create a robust support system for seniors struggling with mental health issues. Programs that emphasize social inclusivity and mental wellness initiatives can provide the necessary resources to enhance mental health awareness among older adults. These initiatives can help reduce stigma and encourage seniors to seek help without feeling isolated or judged.
Community gatherings, support groups, and outreach programs are vital components of these efforts. By involving older adults in conversations about mental health and suicide prevention, communities can foster a culture that values the lives and voices of seniors. Support networks should prioritize establishing connections between older adults and community resources, ensuring that mental health services are readily accessible. Furthermore, providing training to community members about recognizing suicide risk signals can empower them to intervene effectively and provide support.
Mental Health Resources for Older Adults
Improving mental health resources for older adults is crucial in preventing suicide among this vulnerable population. There are numerous organizations and services available, yet many seniors remain unaware or unable to access them. Online directories and resource hubs need to be developed and promoted explicitly for older adults, focusing on reliability and ease of access. This can include helplines, mental health workshops, and direct links to local services that cater specifically to geriatric needs.
Moreover, mental health resources for older adults must emphasize culturally competent care. Considering the diversity in backgrounds and experiences among the elderly, providers who understand these nuances can create more effective outreach and support strategies. Investing in trained professionals who are knowledgeable about geriatric issues can help bridge the gap and create tailored mental health programs that recognize the unique challenges older adults face, ultimately working towards lowering suicide rates.
Innovative Strategies for Suicide Prevention in Later Life
Innovative strategies are essential for rethinking suicide prevention methods tailored specifically for older adults. This includes the use of technology such as mobile applications that allow seniors to easily access mental health resources and support communities. These app-based platforms could offer features like crisis intervention, peer support chatrooms, and mood tracking tools, all designed to meet the unique mental health needs of older adults.
Additionally, training for healthcare providers on geriatric mental health issues is imperative. Workshops and continuing education programs can help practitioners recognize the signs of distress and equip them with intervention skills specifically tailored to older clients. By integrating advanced training with innovative technology solutions, we can enhance overall engagement with mental health care and provide older adults with effective tools to maintain their well-being.
Awareness Campaigns Targeting Geriatric Mental Health
Awareness campaigns targeting geriatric mental health are crucial for reducing suicide risk among seniors. These campaigns should be designed to foster recognition of mental health issues prevalent in older populations, acting as a bridge connecting them to available resources. Social media platforms can be particularly effective for reaching both seniors and their families, driving home the message that mental health matters at every age and encouraging discussions about suicide prevention.
Furthermore, collaborating with influencers and community leaders can amplify the impact of these campaigns. By integrating local voices into awareness efforts, campaigns can resonate more profoundly with the target audience. Using targeted messaging that speaks directly to the experiences and concerns of older adults—such as addressing issues of loneliness and loss—will create more engaging content that prompts seniors to take action and utilize available mental health resources.
Funding and Research Priorities in Elderly Mental Health
Funding and research specific to elderly mental health and suicide prevention are critical in addressing the gaps identified in service delivery. Ensuring that mental health initiatives receive appropriate funding will allow for the development of targeted interventions aimed at older adults. By allocating resources to studies focused on the unique factors influencing elderly mental health, organizations can uncover valuable insights that will inform better practices and policies.
Additionally, increased research into geriatric suicide risk can help to formulate effective prevention programs. Understanding factors such as social isolation or the impact of chronic health conditions can guide the creation of supportive interventions that genuinely meet the needs of older adults. Collaborative studies that involve seniors themselves can provide firsthand accounts of their challenges, paving the way for more effective suicide prevention strategies in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some effective suicide prevention strategies for older adults?
Effective suicide prevention strategies for older adults include increasing awareness of mental health in the elderly, promoting social engagement to combat isolation, and ensuring easy access to mental health resources for older adults. Additionally, implementing targeted outreach campaigns that focus on geriatric suicide awareness can greatly enhance support for this vulnerable population.
How can family members help prevent suicide risk in seniors?
Family members can help prevent suicide risk in seniors by maintaining open lines of communication, offering emotional support, and encouraging older adults to seek help from mental health resources. Regularly checking in, participating in activities together, and recognizing signs of depression can be crucial in addressing mental health concerns in elderly family members.
What online resources are available for suicide prevention for older adults?
There are several online resources focused on suicide prevention for older adults. Websites such as the National Institute of Mental Health and AARP offer valuable information on mental health resources for older adults, including helplines and access to community support services, specifically tailored to address the needs of seniors.
What factors contribute to increased suicide risk in older adults?
Increased suicide risk in older adults can be attributed to factors such as social isolation, chronic health issues, loss of loved ones, and untreated mental health conditions. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for implementing targeted suicide prevention strategies that address the unique challenges faced by this age group.
Why is geriatric suicide awareness important for communities?
Geriatric suicide awareness is important for communities because it fosters understanding and compassion towards older adults who may be experiencing mental health challenges. By raising awareness about the signs of distress and available mental health resources, communities can create a supportive environment that helps reduce stigma and promotes intervention.
What should healthcare providers focus on when addressing suicide prevention for older adults?
Healthcare providers should focus on integrating mental health screening into regular health assessments for older adults, enhancing the availability of tailored mental health resources, and fostering relationships with community support organizations. Recognizing the specific needs of elderly patients is essential for effective suicide prevention efforts.
How can older adults access mental health resources related to suicide prevention?
Older adults can access mental health resources related to suicide prevention through their healthcare providers, local senior centers, and online platforms that offer tailored support. Many organizations provide helplines and online support groups that cater specifically to the needs of seniors, ensuring that help is accessible and relevant.
What role does social engagement play in reducing suicide risk among older adults?
Social engagement plays a crucial role in reducing suicide risk among older adults by combating feelings of loneliness and isolation, which are common in this population. Participating in community activities, maintaining relationships, and having regular social interactions can significantly enhance mental health and overall well-being in older adults.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Older Adults at Risk | Adults aged 75 and older have the highest suicide rates among age groups, highlighting their urgent needs. |
| Lack of Resources | There are few accessible online resources targeted specifically for older adults seeking suicide prevention support. |
| Research Findings | A study from McLean Hospital revealed an imbalance in online suicide prevention efforts, under-serving older adults despite their high risk. |
| Community Needs | Older adults often experience social isolation and may feel overlooked in research, increasing their risk for suicide. |
| Call for Action | The study calls for public health campaigns tailored to older adults and the need for increased funding for targeted suicide prevention. |
| Support for Research | Funding has been obtained from various health institutes and charitable foundations to further suicide prevention research for older adults. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a crucial issue, as this demographic faces the highest rates of suicide yet has limited access to adequate resources. The study conducted by researchers at McLean Hospital reveals the significant gap in targeted suicide prevention efforts for older adults, particularly those aged 75 and above. Addressing these disparities requires immediate action through tailored campaigns and increased funding to ensure effective support systems that cater to the unique needs of this vulnerable population.