Pregnancy-Related Deaths: A Call for Urgent Action
In recent years, pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. have come under intense scrutiny as the nation grapples with a soaring maternal mortality rate, significantly higher than other high-income countries. Alarmingly, more than 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, yet the situation continues to worsen, with data revealing increases from 2018 to 2022. The disparities in maternal health outcomes are stark, varying greatly by state and among racial and ethnic groups, underscoring systemic health disparities within the American healthcare framework. Significant contributors to these tragic outcomes include inadequate prenatal care and a lack of extended postpartum support, particularly for those at risk of cardiovascular disease. Addressing these issues is crucial, as focusing on quality prenatal and postpartum care could drastically reduce the incidence of pregnancy-related deaths and improve overall maternal health across the country.
Pregnancy-related fatalities have emerged as a pressing public health issue, intertwined with the broader domain of maternal health challenges. The alarming rise in maternal deaths necessitates a deeper exploration of associated factors, including inadequate maternity care, socioeconomic inequalities, and chronic health conditions prevalent among expectant mothers. The need for accessible prenatal and postpartum resources is paramount to mitigate these risks and ensure that all women receive equitable care during and after their pregnancies. The growing prevalence of issues such as cardiovascular complications among pregnant individuals calls for immediate attention and policy changes to enhance preventive measures. Ultimately, tackling the complexities surrounding maternal mortality is vital for fostering a healthier future for mothers and their children.
Understanding the Rising Rates of Pregnancy-Related Deaths in the U.S.
The alarming rise in pregnancy-related deaths in the United States has drawn attention from health professionals and researchers alike. Recent studies indicate that the U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with preventable deaths making up over 80% of the statistics. Researchers attribute this tragic trend to several factors, including systemic health disparities that adversely affect marginalized groups. Furthermore, the intersection of chronic health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, and social determinants of health contribute to the increased risk of maternal mortality among specific demographics.
State-by-state disparities further complicate the issue, as maternal mortality rates vary dramatically across the country. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience mortality nearly four times higher than that of their white counterparts. These stark differences highlight the urgent need for comprehensive prenatal care and targeted interventions that consider the diverse backgrounds and health profiles of expectant mothers. Without addressing these disparities, the upward trend in pregnancy-related deaths is likely to continue.
The Importance of Comprehensive Prenatal and Postpartum Care
Effective maternity care is essential for improving maternal health outcomes and preventing pregnancy-related deaths. Comprehensive prenatal care ensures that pregnant individuals receive the necessary screenings, education, and resources to manage their health conditions throughout pregnancy. Additionally, extending postpartum care beyond the traditional six-week check-up is crucial, as many complications arise in the months following childbirth. The World Health Organization advocates for a broader definition of maternal mortality that includes late maternal deaths, recognizing that postpartum recovery is a critical period requiring ongoing support and monitoring.
Investments in both prenatal and postpartum care can significantly reduce the maternal mortality rate. By adopting innovative care models that incorporate continuous health assessments and community support, healthcare systems can ensure that new mothers receive appropriate resources and interventions. Moreover, addressing the social and economic factors that contribute to health disparities can lead to more equitable health outcomes for all pregnant individuals. Ensuring access to quality care must become a priority in public health agendas to effectively combat rising rates of maternal mortality.
Addressing Health Disparities in Maternal Care
Health disparities are a driving force behind the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths among different racial and ethnic groups in the U.S. The data clearly shows that American Indian, Alaska Native, and non-Hispanic Black women face significantly higher risks of maternal mortality compared to their white counterparts. These disparities are largely the result of socio-economic factors, systemic racism, and barriers to accessing quality healthcare. It is imperative to identify and address these inequities within the healthcare system to improve outcomes for marginalized groups.
Targeted interventions and policy changes are necessary to dismantle the barriers that perpetuate health disparities. This can include increasing funding for maternal health programs that specifically serve high-risk communities, expanding access to health insurance, and incorporating culturally competent care practices into prenatal services. By leveraging data to inform policy decisions and targeting resources where they are most needed, stakeholders can work toward a healthcare system that better supports all women during pregnancy and the postpartum period.
Role of Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Cardiovascular disease has emerged as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths in the United States, accounting for over 20% of these fatalities. The shift from hemorrhage to cardiovascular complications as the primary risk signals a growing public health concern, particularly as more young people are diagnosed with chronic conditions like hypertension. These health issues can complicate pregnancies and increase the risk of adverse outcomes, underscoring the need for effective management of cardiovascular conditions before and during pregnancy.
To combat the rising incidence of maternal deaths related to cardiovascular disease, healthcare providers must prioritize early screenings and interventions for all pregnant individuals. This includes educating expectant mothers about lifestyle factors contributing to heart health and routinely monitoring blood pressure throughout pregnancy. By addressing cardiovascular health proactively, the healthcare system can significantly mitigate the risks associated with pregnancy-related complications and ultimately improve maternal health outcomes.
Public Health Infrastructure and Maternal Health Funding
Investing in robust public health infrastructure is crucial for tracking and improving maternal health outcomes across the United States. The lack of a consistent national system to monitor maternal mortality rates until 2018 highlights a significant gap in public health data. Without comprehensive data collection, it is challenging to understand the full scope of pregnancy-related deaths and implement effective interventions. Continuous investment in maternal health research is essential for developing evidence-based strategies that can effectively reduce mortality rates.
In light of recent budget cuts to public health programs, it is vital that stakeholders advocate for increased funding and policy support aimed at enhancing maternal healthcare services. Collaborative efforts among government agencies, healthcare providers, and community organizations can lead to more informed policymaking and improved access to care. By prioritizing maternal health in public health initiatives, the U.S. can work toward reversing the troubling trends in pregnancy-related deaths.
Innovative Solutions to Improve Maternal Health Outcomes
To address the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths and improve maternal health outcomes, innovative solutions must be implemented across the healthcare system. This includes utilizing telehealth services to enhance access to prenatal and postpartum care, particularly in rural and underserved areas. Telehealth can provide critical health information, support, and ongoing monitoring for expectant and new mothers when they may face barriers to in-person visits.
Moreover, integrating community-based programs that offer education and resources for mothers can empower them with the knowledge and skills to manage their own health during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Customized programs that address the specific needs of diverse populations can help reduce disparities and improve pregnancy outcomes. By tapping into technology and community resources, the healthcare system can foster a more supportive environment for mothers and ensure they receive the comprehensive care they need.
The Importance of Mental Health in Maternal Care
Mental health is a critical component of comprehensive maternity care, yet it often remains overlooked in discussions about pregnancy-related deaths. Conditions such as postpartum depression and anxiety can have profound impacts on a mother’s wellbeing and her ability to care for herself and her newborn. Addressing mental health needs during the prenatal and postpartum periods is essential to improving overall maternal health outcomes and ensuring a positive transition to motherhood.
Integrating mental health screenings and support services into routine prenatal and postpartum care can help identify at-risk mothers and provide the necessary interventions early on. Collaborative care models that involve obstetricians, mental health providers, and community supports can facilitate a more holistic approach to maternal health, recognizing the interconnectedness of physical and mental wellbeing. By prioritizing mental health in maternity care, we can help reduce the risk of pregnancy-related deaths and foster healthier families.
The Role of Education in Reducing Maternal Mortality
Education plays a pivotal role in reducing maternal mortality rates and improving health outcomes for pregnant individuals. Comprehensive education programs that cover the significance of prenatal care, postpartum recovery, and the warning signs of complications can empower mothers to seek help when needed. Increasing knowledge about maternal health risks, particularly in high-risk populations, can lead to earlier interventions and better management of health conditions throughout pregnancy.
Moreover, educational outreach initiatives that target underserved communities can help bridge gaps in access to care and resources. By providing relevant information in culturally sensitive ways, healthcare providers can engage expectant mothers and their families more effectively. This approach not only helps in identifying potential health issues but also fosters a sense of agency among mothers in managing their health, ultimately aiming to decrease rates of preventable pregnancy-related deaths.
Advocating for Policy Changes to Enhance Maternal Health
Advocacy for policy changes is essential to enhance maternal health services and address the growing rates of pregnancy-related deaths in the United States. Engaging with policymakers, health organizations, and community leaders can lead to the development of targeted policies aimed at reducing disparities and improving access to quality prenatal and postpartum care. Collaborative efforts can drive legislative changes that prioritize maternal health and allocate resources to tackle the systemic issues contributing to high mortality rates.
Furthermore, advocacy efforts should focus on ensuring that maternal health is treated as a public health priority. This involves raising awareness about the importance of equitable care across all states and addressing the unique challenges faced by different demographics. By rallying support for comprehensive strategies that include data-driven policy-making and community engagement, we can work towards creating a healthcare environment that protects every individual’s right to quality maternal care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The primary causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. include cardiovascular diseases, hemorrhage, and infections. Cardiovascular disease alone accounts for over 20% of these deaths, highlighting the need for better prenatal care and management of chronic conditions.
How does the maternal mortality rate in the U.S. compare to other high-income countries?
The maternal mortality rate in the U.S. is higher than in any other high-income country, with significant racial and state-based disparities. Efforts to improve prenatal care and postpartum care could help reduce these alarming rates.
What role do health disparities play in pregnancy-related deaths?
Health disparities significantly impact pregnancy-related deaths, with women of color—particularly American Indian, Alaska Native, and Black women—experiencing much higher mortality rates. Addressing these disparities is essential for reducing the overall maternal mortality rate.
Why is postpartum care important in preventing pregnancy-related deaths?
Postpartum care is crucial as many pregnancy-related deaths occur after six weeks postpartum. Improvement in postpartum health services can address chronic conditions and provide ongoing support to reduce maternal mortality.
How can cardiovascular disease contribute to pregnancy-related deaths?
Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, affecting women during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Conditions like hypertension and cardiomyopathy have become more prevalent among younger women, necessitating targeted prenatal and postpartum care.
What measures can be taken to lower the rising rates of pregnancy-related deaths?
To lower pregnancy-related deaths, it’s vital to enhance public health infrastructure, improve access to comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care, and address health disparities across racial and ethnic groups.
What is the significance of ‘late maternal deaths’ in relation to pregnancy-related mortality?
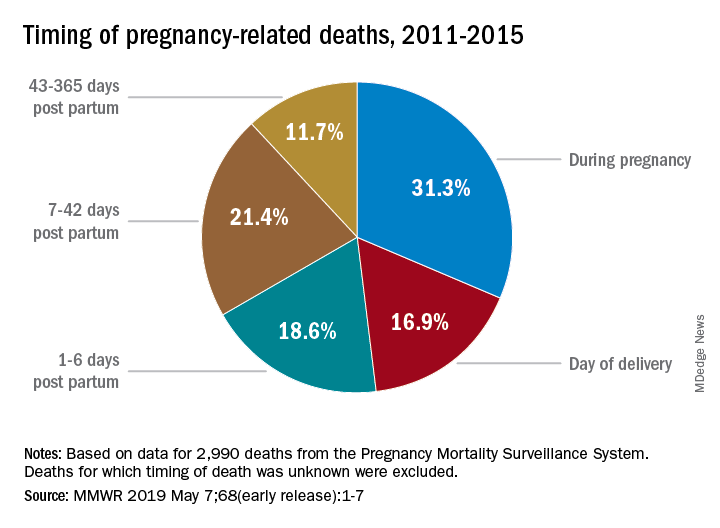
‘Late maternal deaths,’ occurring between 42 days and one year postpartum, accounted for nearly a third of maternal deaths in recent studies. Recognizing these deaths emphasizes the importance of continuous healthcare support beyond the traditional six-week postpartum period.
What strategies can effectively reduce maternal mortality rates in the United States?
Effective strategies to reduce maternal mortality rates include increasing healthcare access, implementing systemic changes in care delivery, funding maternal health research, and creating policies that specifically focus on quality of care during both pregnancy and postpartum periods.
How does access to quality prenatal care affect pregnancy-related deaths?
Access to quality prenatal care is critical in identifying and managing potential health risks during pregnancy. Improved prenatal services can help prevent complications that lead to pregnancy-related deaths.
What changes are needed in healthcare policies to address pregnancy-related mortality?
Healthcare policies must focus on equitable access to maternal healthcare, particularly in underserved areas, as well as invest in maternal health programs that enhance care quality during pregnancy and beyond.
| Key Points | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Rising Rates of Pregnancy-Related Deaths | Between 2018-2022, rates increased, with a notable rise in 2021, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. | |
| High Preventability | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. | |
| Disparities by Race and Geography | Significant disparities exist, especially for American Indian and Alaska Native women, who have the highest mortality rates. | |
| Leading Causes of Death | Cardiovascular disease is now the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths. | |
| Importance of Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths (42 days to 1 year postpartum) account for nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths. | |
| Need for Systemic Change | Investment in public health infrastructure and policy changes are crucial to address rising rates. | |
| Call to Action | Focus on improving quality of care during pregnancy and the postpartum period while addressing state-level disparities. | |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths are a growing concern in the U.S., highlighting a critical public health issue that requires immediate attention. Despite the fact that most of these fatalities are preventable, the nation leads high-income countries in maternal mortality rates, with alarming disparities across different states and racial groups. The ongoing need for comprehensive healthcare reforms, better access to prenatal and postpartum care, and focused interventions aimed at inequities is essential to address this pressing issue. If significant changes are not implemented, the upward trend in pregnancy-related deaths is likely to continue.
You may also like
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | 31 | |||||