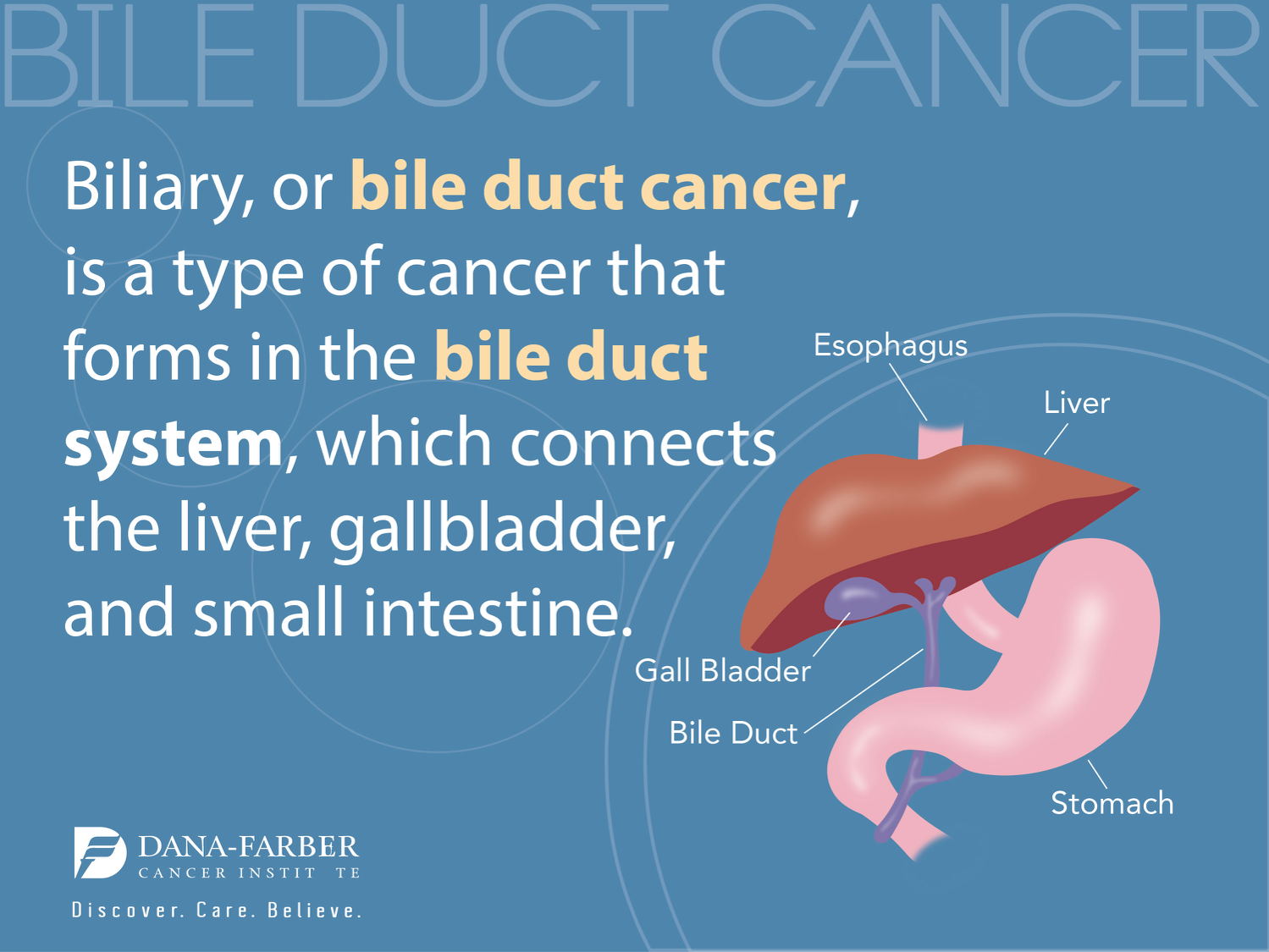
Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer: Key Findings Revealed
Bile imbalance is increasingly recognized as a crucial factor in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of this disease. Recent studies have linked unhealthy bile acid metabolism to various liver conditions, shedding light on potential causes of liver cancer. The connection between bile acids and liver disease encompasses key molecular mechanisms, including the regulation of the YAP FXR connection, which plays a pivotal role in controlling bile homeostasis. Disruptions in this balance can result in severe consequences, such as liver inflammation and ultimately cancer. Understanding these connections not only highlights the importance of bile in liver health but also opens the door to novel liver disease treatment options that target these underlying mechanisms.
The disruption of bile production and regulation is gaining momentum as a critical area of investigation for liver-related diseases, particularly when it concerns malignant conditions such as liver cancer. Investigators are delving into bile acid dysfunction as a significant factor contributing to hepatocellular carcinoma, leveraging knowledge about bile’s multiple roles beyond digestion. This exploration includes examining how the interplay between biological signals—namely the YAP and FXR pathways—affects liver health. Furthermore, researchers are uncovering how an excess of bile acids can destabilize liver function, leading to serious complications. By identifying new pathways for regulatory intervention, there is a growing interest in developing innovative strategies for liver disease treatment.
Understanding Liver Cancer Causes: The Role of Bile Imbalance
Liver cancer remains one of the leading health concerns globally, with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) being the most prevalent type. Research has increasingly highlighted the significant role of bile acid metabolism in the development of liver diseases. Disruptions in bile acid homeostasis can lead to an imbalance that promotes inflammation and injury in liver tissues. This imbalance results not only from the overproduction of bile acids but also from the failure of the liver to effectively excrete these acids, thus fostering an environment conducive to liver cancer.
A critical mechanism underlying this process involves the YAP-FXR connection, where the YAP protein negatively regulates the FXR receptor, essential for bile acid regulation. This dysregulation can lead to a cascade of events including liver fibrosis and ultimately cancerous transformations in liver cells. It is therefore imperative to understand these molecular interactions as they provide insight into potential therapeutic targets for liver cancer treatment.
Bile Acid Metabolism: Key to Liver Disease Treatment Options
Bile acid metabolism plays a crucial role in determining the severity and progression of liver diseases, including the onset of hepatocellular carcinoma. Current treatment options for liver cancer are evolving as scientists discover more about how bile acids influence liver health. The recognition that targeting the YAP pathway can improve bile acid regulation opens the door for innovative treatment strategies. By enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion through various pharmacological interventions, it may be possible to halt or even reverse the progression of liver damage and cancer.
Additionally, recent advancements have led to the development of therapies that aim to restore the natural balance of bile acids in individuals suffering from liver diseases. These treatments could mitigate the detrimental effects of bile imbalance, reducing inflammation and preventing fibrosis, thereby lowering the risk of developing liver cancer. As research continues, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to stay informed about these emerging treatment options, as they may transform the landscape of liver disease management.
The YAP-FXR Connection: A Newly Identified Molecular Switch
The intricate relationship between the YAP protein and the FXR receptor has garnered significant interest in the field of liver cancer research. The identification of this connection as a molecular switch highlights the complexity of cell signaling pathways involved in bile acid metabolism. When YAP is activated, it not only disrupts FXR function but also instigates a series of metabolic disturbances leading to liver injury. Understanding the nuances of this interaction can provide novel insights into cancer biology and the roles of metabolic processes in tumorigenesis.
Research suggests that therapeutic strategies targeting this YAP-FXR axis may offer new avenues for intervention in liver diseases. By blocking YAP’s repressive effects on FXR, researchers are optimistic about restoring balance to bile acid metabolism, which could enhance liver function and diminish the likelihood of tumor formation. The implications are profound, as they may lead to the development of drugs specifically designed to modulate these signaling pathways, ultimately improving outcomes for patients with liver cancer.
Importance of Bile Acids in Metabolic Processes
Bile acids serve multiple critical functions beyond aiding fat digestion; they are also integral players in various metabolic processes in the liver. These compounds act as signaling molecules and have been shown to influence glucose metabolism, lipid homeostasis, and inflammation. Their complex role in metabolism underscores why maintaining proper bile acid levels is essential for overall liver health and disease prevention. A disturbance in bile acid dynamics can lead to increased risks of chronic liver conditions, highlighting the need for comprehensive understanding and management of bile acid metabolism.
Moreover, research into bile acids has led to emerging insights regarding their potential as therapeutic agents. Certain bile acid derivatives are being investigated for their capabilities to modulate metabolic pathways and alleviate liver conditions. As science progresses, the future appears promising for exploring how bile acids can be harnessed for new treatment options in liver diseases, paving new paths in oncology and hepatology.
Exploring Experimental Models: Experimental Findings on Liver Damage
Experimental models are crucial in elucidating the mechanisms that lead to liver cancer, allowing researchers to simulate the complex interactions of various bio-molecules such as bile acids and signaling proteins like YAP and FXR. Recent studies have demonstrated that manipulations within these pathways can result in significant reductions in liver damage and cancer progression in preclinical models. For instance, activating FXR and inhibiting YAP repressive activities have shown marked improvements in liver health, providing evidence for the development of new drugs targeting these pathways.
These experimental findings highlight how controlled laboratory settings can drive our understanding of liver diseases, providing essential data on how bile acid homeostasis affects liver cancer outcomes. The implications of such research extend beyond the lab, promising potential breakthroughs in clinical practices and treatments for those affected by liver conditions.
Future Directions in Liver Cancer Research: Targeting Bile Acid Dynamics
As the link between bile imbalance and liver cancer becomes more evident, the future of liver cancer research is likely to emphasize innovative strategies that target bile acid dynamics. The understanding that YAP’s inhibition of FXR plays a pivotal role in liver cancer initiation prompts further investigation into how adjusting bile acid flows could be beneficial. Newer therapeutic approaches may focus on pharmacological agents that can enhance FXR functionality or stimulate bile acid export, ultimately mitigating liver cancer risks.
Furthermore, exploring the connections between bile acids and other signaling pathways could lead to a more holistic understanding of liver disease and open avenues for multifaceted treatment regimens. Research in this area will be paramount in developing integrated approaches to liver disease prevention, paving the way for more effective interventions against liver cancer.
Bile Acid Excretion: A Key Factor in Liver Health
Efficient bile acid excretion is essential for maintaining liver health and preventing the onset of diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma. Disruptions in this process can result in the accumulation of toxic bile acids, leading to liver inflammation and fibrosis. Addressing bile acid excretion mechanisms could offer promising therapeutic strategies for managing liver conditions by alleviating the pressure on liver function.
Current research is focusing on understanding the transport proteins involved in bile acid export, such as the bile salt export pump (BSEP). Enhancing the function of these export proteins could improve bile acid clearance and thus enhance liver function, leading to better clinical outcomes for patients at risk of liver cancer. This focus not only extends treatment options but also opens new avenues for preventative care in at-risk populations.
The Impact of Inflammation on Liver Cancer Progression
Chronic inflammation has been established as a significant contributor to liver cancer progression, particularly in cases associated with bile acid imbalance. The pathophysiological relationship between ongoing inflammation and liver cancer underscores the need for integrated treatment approaches that address both factors. Inflammatory cytokines and other mediators can further exacerbate bile acid dysregulation, creating a vicious cycle that increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Targeting inflammation could serve as a dual approach in treating liver diseases characterized by bile imbalances. Therapies aimed at reducing inflammation not only aim to mitigate liver injury but also help restore normal bile acid metabolism. The potential for combining anti-inflammatory agents with approaches that target bile functionality may revolutionize liver health management.
Synergistic Approaches to Liver Cancer Treatment
Understanding the diverse pathways involved in bile acid metabolism and liver cancer paves the way for synergistic treatment approaches. By combining therapies that target different aspects of liver function—such as restoration of bile acid homeostasis and inhibition of the YAP repressive pathway—researchers are looking to create integrated solutions that enhance patient outcomes. This multidimensional strategy is particularly relevant given the complexity of liver diseases and their underlying causes.
Furthermore, there’s growing interest in utilizing dietary and lifestyle interventions that support healthy bile acid metabolism within concurrent treatment regimens. Given that lifestyle factors significantly influence metabolic health, combining pharmaceutical interventions with dietary management may maximize therapeutic efficacy and offer holistic management strategies for individuals at risk of liver cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer causes?
Bile imbalance can significantly contribute to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The liver produces bile, which aids in fat digestion, but an imbalance can lead to excessive bile acid accumulation, causing liver injury, inflammation, and eventually cancer. Disruptions in bile acid metabolism are critical factors in the development of liver diseases.
How does bile acid metabolism relate to liver cancer progression?
Bile acid metabolism is closely linked to liver cancer progression through the regulation of important signaling pathways. An imbalance can activate YAP, which inhibits FXR—a vital component in maintaining bile acid homeostasis. This impairment may lead to liver fibrosis and inflammation, ultimately increasing the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
What role does the YAP FXR connection play in liver disease?
The YAP FXR connection is pivotal in liver disease as it governs bile acid metabolism. Activation of YAP can disrupt FXR’s ability to manage bile acid levels, resulting in an accumulation that fosters liver damage and the potential progression to liver cancer. Understanding this connection may lead to innovative treatment strategies for liver diseases.
What are potential liver disease treatment options targeting bile imbalance?
Treatment options for liver diseases associated with bile imbalance may include therapies that enhance FXR function, inhibit YAP activation, or increase bile acid excretion. These strategies aim to restore bile acid homeostasis, reduce liver damage, and mitigate the risks of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
How can understanding bile acid metabolism contribute to liver cancer prevention?
By understanding bile acid metabolism’s role in liver cancer development, researchers can identify therapeutic targets to prevent hepatocellular carcinoma. Addressing bile imbalance through pharmacological interventions that promote FXR activity or enhance bile acid excretion may significantly reduce the risk and progression of liver cancer.
What findings did researchers discover about bile imbalance and liver cancer treatment?
Researchers found that blocking YAP’s repressor activity, which disrupts bile acid sensing, offers a promising avenue for liver cancer treatment. Enhancing FXR function and promoting bile acid excretion could potentially halt liver damage and cancer progression by reestablishing bile homeostasis, leading to novel therapeutic strategies.
Why is the relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer important for future research?
The relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer is crucial for future research as it uncovers pathways that can be targeted for treatment and prevention. Understanding the mechanisms of bile acid metabolism and its regulatory factors opens doors to developing innovative therapies that could significantly impact liver disease outcomes and reduce liver cancer risk.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A critical imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Role of Bile | Bile aids in fat digestion and functions similarly to hormones that influence metabolic processes. |
| Key Researcher | Yingzi Yang, a professor at Harvard, studied the regulation of bile acid production and its link to liver injury and cancer. |
| Molecular Mechanism | YAP, a protein that regulates cell growth, disrupts bile acid metabolism and hampers the FXR receptor, leading to liver cancer. |
| Potential Treatment Approaches | Blocking YAP’s repressive action or enhancing FXR function may provide new strategies to prevent liver cancer. |
| Research Significance | Findings suggest pharmacological avenues to stimulate FXR and highlight the link between cellular signaling and liver diseases. |
Summary
Bile imbalance and liver cancer are closely linked, as recent studies reveal the role of bile acids in triggering liver diseases like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The findings underscore the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis and present new potential therapeutic strategies to combat liver cancer by targeting the key molecular processes involved.
You may also like
Archives
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | 31 | |||||